这里以一道题目为例
题目描述
Alice 和 Bob 现在要乘飞机旅行,他们选择了一家相对便宜的航空公司。该航空公司一共在 $n$ 个城市设有业务,设这些城市分别标记为 $0$ 到 $n-1$,一共有 $m$ 种航线,每种航线连接两个城市,并且航线有一定的价格。
Alice 和 Bob 现在要从一个城市沿着航线到达另一个城市,途中可以进行转机。航空公司对他们这次旅行也推出优惠,他们可以免费在最多 $k$ 种航线上搭乘飞机。那么 Alice 和 Bob 这次出行最少花费多少?
输入格式
第一行三个整数 $n,m,k$,分别表示城市数,航线数和免费乘坐次数。
接下来一行两个整数 $s,t$,分别表示他们出行的起点城市编号和终点城市编号。
接下来 $m$ 行,每行三个整数 $a,b,c$,表示存在一种航线,能从城市 $a$ 到达城市 $b$,或从城市 $b$ 到达城市 $a$,价格为 $c$。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数,为最少花费。
样例输入
5 6 1
0 4
0 1 5
1 2 5
2 3 5
3 4 5
2 3 3
0 2 100样例输出
8数据规模与约定
对于 $30\%$ 的数据,$2 \le n \le 50$,$1 \le m \le 300$,$k=0$。
对于 $50\%$ 的数据,$2 \le n \le 600$,$1 \le m \le 6\times10^3$,$0 \le k \le 1$。
对于 $100\%$ 的数据,$2 \le n \le 10^4$,$1 \le m \le 5\times 10^4$,$0 \le k \le 10$,$0\le s,t,a,b < n$,$a\ne b$,$0\le c\le 10^3$。
另外存在一组 hack 数据。
区别与一般的单图问题,这道题中我们需要考虑可以免费坐飞机的航线
相当于每个节点都存在一个状态,即到这个节点还能免费坐飞机的次数
拥有相同状态的节点共同组成一张图
所以需要对寻路的方式进行部分修改,这里采用优先队列的Dijkstra最短路算法
struct node
{
int dw, dnode, cnt;
bool operator<(const node& a)const {
return dw > a.dw;
}
};构造优先队列 priority_queue 使用的结构体,并重载小于号
其中存储了这个节点的编号dnode ,节点到起始点的距离 dw ,以及当前节点使用的免费次数 cnt
int dis[20010][12];
bool vis[20010][12];同样的,记录最短距离的 dis 和记录访问节点的 vis 数组都需要根据状态的不同来进行分层操作
void dijkstra(int st) {
init();
q.push({ 0, st, 0 });
dis[st][0] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
const node ttop = q.top();
q.pop();
if (vis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt]) continue;
vis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] = 1;
for (auto it = e[ttop.dnode].begin(); it != e[ttop.dnode].end(); it++) {
if (ttop.cnt < k&& dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt]) {
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt];
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1],it->v,ttop.cnt + 1 });
}
if (dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w) {
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w;
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt],it->v,ttop.cnt });
}
}
}
}除了松弛操作外,多层图和单图的源码几乎相同,都采用了优先队列贪心来找当前最优的节点
在松弛操作内,我们需要考虑当前的节点能否使用免费的次数,免费后是不是最优
- 当前的节点可以免费
if (ttop.cnt < k&& dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt]) {//判断是不是最优
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt];//如果能更新最短路径,那就更新
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1],it->v,ttop.cnt + 1 });//将更新后的节点放入队列,注意状态也要更新
}- 当前的节点不能免费或不采取免费
if (dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w) {//判断能否更新
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w;
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt],it->v,ttop.cnt });//放入更新后的节点
}Dijkstra寻路结束后,我们遍历一遍终点节点的所有状态,找到一个最小的dis[ed][i],即最优解
int ans = 1e9;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) ans = min(ans, dis[ed][i]);
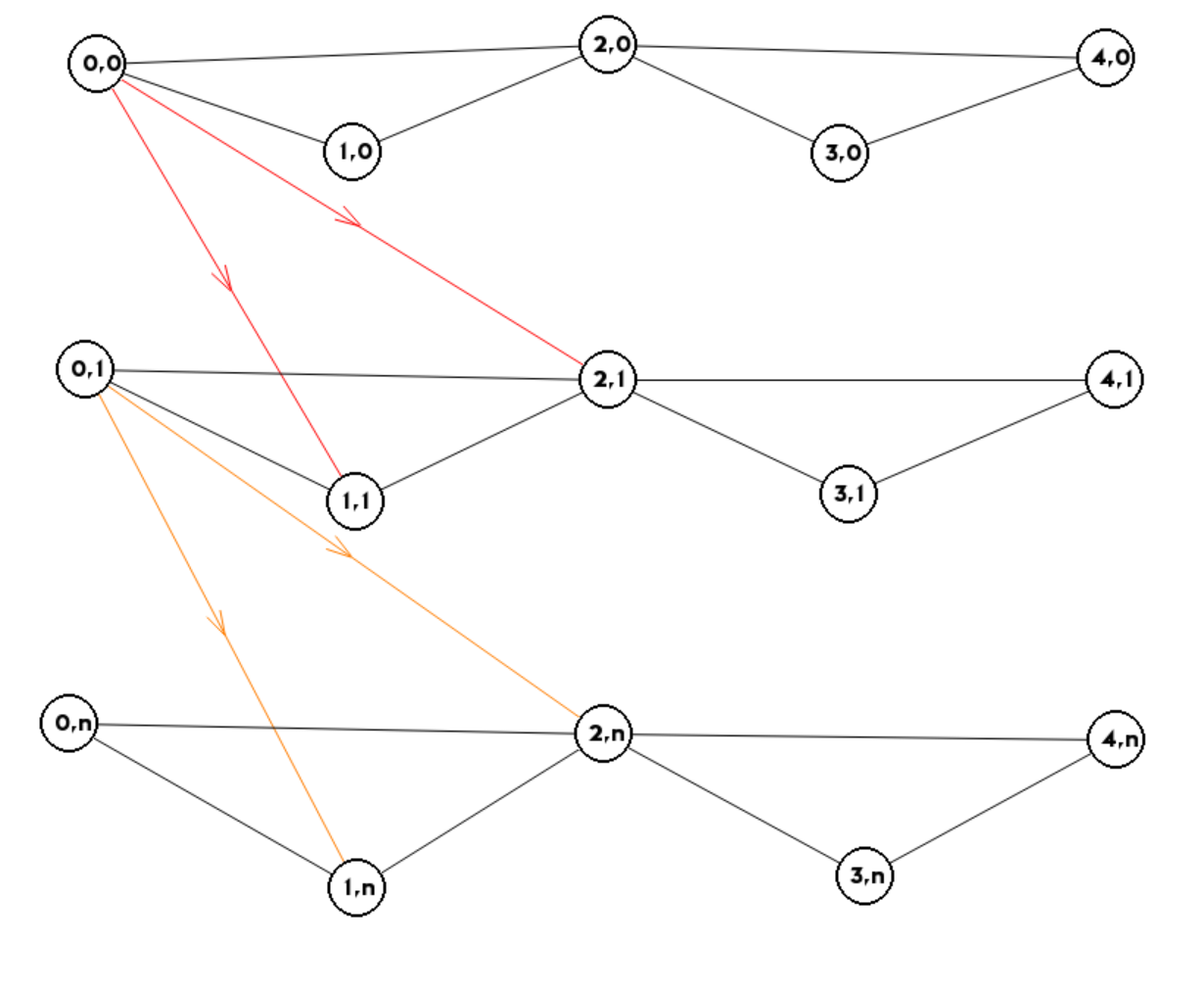
图上的每一个节点都有向下层的可联通节点前进的无权边(免费)
上图以 $0$ 号节点为例,它可以通过免费次数构建出来的边向下层图移动,直到免费次数用尽
总而言之,解决分层图的关键就在建图,需要正确地通过不同的状态构造出图
完整代码:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define streampreset() ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int v, w;
};
struct node
{
int dw, dnode, cnt;
bool operator<(const node& a)const {
return dw > a.dw;
}
};
int n, m, k;
int st, ed;
vector<edge> e[50010];
priority_queue<node> q;
int dis[20010][12];
bool vis[20010][12];
void insert(int u, int v, int w) {
e[u].push_back({ v,w });
}
void init(void) {
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis);
}
void dijkstra(int st) {
init();
q.push({ 0, st, 0 });
dis[st][0] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
const node ttop = q.top();
q.pop();
if (vis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt]) continue;
vis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] = 1;
for (auto it = e[ttop.dnode].begin(); it != e[ttop.dnode].end(); it++) {
if (ttop.cnt < k&& dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt]) {
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt];
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt + 1],it->v,ttop.cnt + 1 });
}
if (dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] > dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w) {
dis[it->v][ttop.cnt] = dis[ttop.dnode][ttop.cnt] + it->w;
q.push({ dis[it->v][ttop.cnt],it->v,ttop.cnt });
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
streampreset();
cin >> n >> m >> k >> st >> ed;
int u, v, w;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v >> w;
insert(u, v, w);
insert(v, u, w);
}
dijkstra(st);
int ans = 1e9;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) ans = min(ans, dis[ed][i]);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
评论区(暂无评论)